The Dutch Hunger Winter Case Study Answers provide a comprehensive analysis of the devastating famine that occurred in the Netherlands during the winter of 1944-1945. This case study examines the historical context, causes, impact, relief efforts, and lessons learned from this tragic event, offering valuable insights into the importance of food security and preparedness.
The German occupation of the Netherlands during World War II led to a severe food shortage, resulting in widespread hunger and malnutrition. The famine had profound physical and psychological effects on the Dutch population, with an estimated 20,000 to 22,000 deaths attributed to starvation.
Historical Context
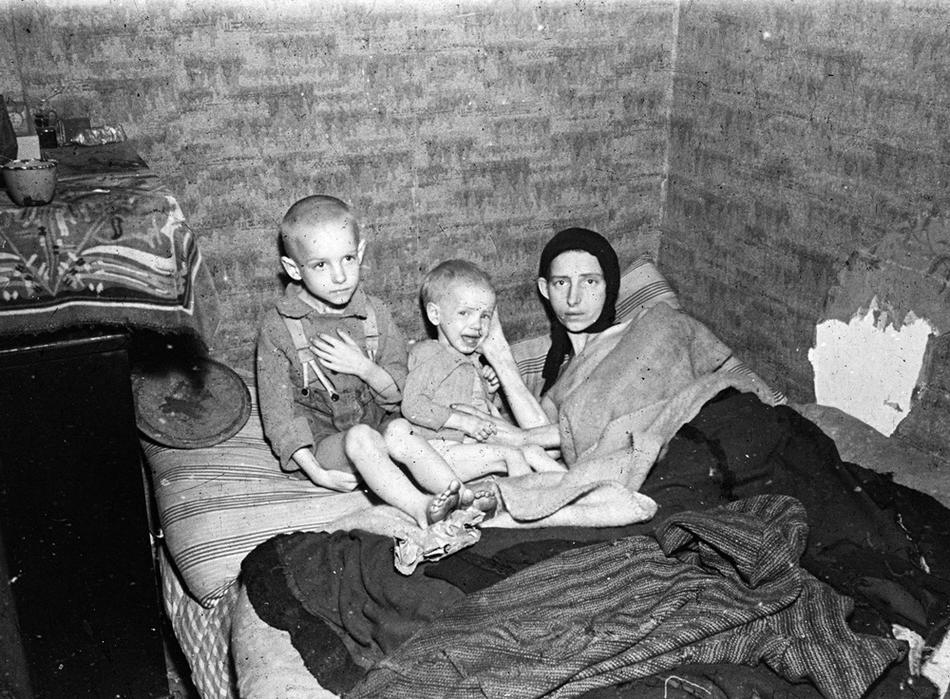

The winter of 1944-1945 in the Netherlands was a period of extreme hardship and starvation known as the Dutch Hunger Winter. The country was occupied by Nazi Germany during World War II, and the German occupiers implemented a series of policies that led to a severe food shortage.
Role of the German Occupation
The German occupation of the Netherlands began in May 1940. The Germans quickly imposed a strict rationing system on the Dutch population, and they also confiscated large amounts of food from the country. This left the Dutch people with very little to eat, and the situation was made worse by the fact that the Germans also blocked all food imports into the country.
Causes of the Famine
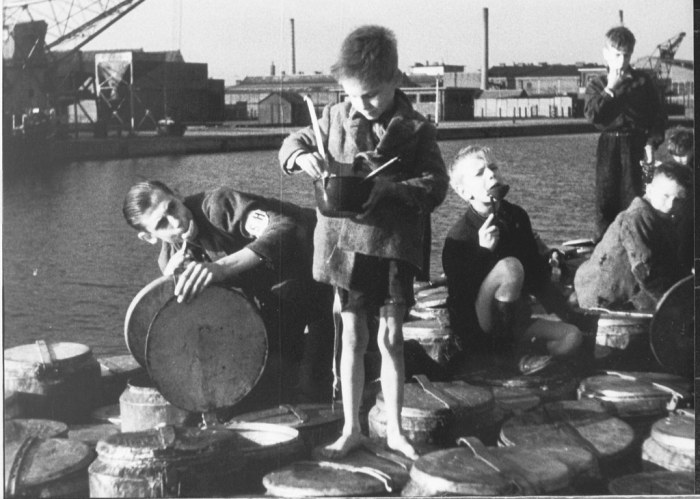

The Dutch Hunger Winter was caused by a combination of factors, including the German occupation, the Dutch government’s policies, and the harsh winter weather.
Impact of the German Blockade
The German blockade of the Netherlands was the most significant factor in the Dutch Hunger Winter. The blockade prevented food from entering the country, and it also made it difficult for the Dutch people to grow their own food.
Role of the Dutch Government’s Policies
The Dutch government also played a role in the famine. The government’s rationing system was inefficient, and it failed to provide the Dutch people with enough food. The government also made the mistake of not stockpiling food before the war, which left the country vulnerable to food shortages.
Impact of the Famine
The Dutch Hunger Winter had a devastating impact on the Dutch population. An estimated 20,000 people died from starvation or related illnesses, and many more suffered from malnutrition.
Physical and Psychological Effects
The physical effects of the famine included weight loss, edema, and vitamin deficiencies. The psychological effects included depression, anxiety, and apathy.
Social and Economic Consequences
The famine also had a significant social and economic impact on the Netherlands. The death and illness of so many people weakened the country’s workforce and economy. The famine also led to a loss of trust in the government.
Relief Efforts
The Dutch government and international organizations made several efforts to provide relief to the starving population during the Dutch Hunger Winter. These efforts included distributing food, providing medical care, and setting up soup kitchens.
Challenges Faced
The relief efforts were hampered by a number of challenges, including the German blockade, the harsh winter weather, and the lack of resources.
Effectiveness of the Relief Efforts
Despite the challenges, the relief efforts did help to save lives. The distribution of food and medical care helped to reduce the number of deaths from starvation and related illnesses.
Lessons Learned: The Dutch Hunger Winter Case Study Answers
The Dutch Hunger Winter is a reminder of the importance of food security and preparedness. It is also a reminder of the importance of government policies in preventing and mitigating famines.
Importance of Food Security and Preparedness
The Dutch Hunger Winter showed that it is essential for countries to have a secure food supply. Countries should have a plan in place to ensure that they have enough food to feed their population, even in times of crisis.
Role of Government Policies, The dutch hunger winter case study answers
The Dutch Hunger Winter also showed that government policies can play a significant role in preventing and mitigating famines. Governments should have policies in place to ensure that their population has access to enough food, even in times of crisis.
FAQ Summary
What were the primary causes of the Dutch Hunger Winter?
The primary causes of the Dutch Hunger Winter were the German blockade of the Netherlands, which cut off food supplies, and the harsh winter conditions, which made food distribution difficult.
What were the physical and psychological effects of the famine on the Dutch population?
The famine caused widespread hunger, malnutrition, and disease. It also led to increased mortality rates, particularly among children and the elderly.
What lessons were learned from the Dutch Hunger Winter?
The Dutch Hunger Winter highlighted the importance of food security and preparedness, as well as the role of government policies in preventing and mitigating famines. It also emphasized the need for international cooperation in humanitarian emergencies.