Lesson 14 analyzing the structure of a poem answer key – Embark on a captivating journey into the intricacies of poetry as we delve into Lesson 14: Analyzing the Structure of a Poem. This comprehensive guide unveils the essential components that shape a poem’s architecture, empowering you to decipher the profound impact of structure on meaning and impact.
Through a series of insightful examples and expert analysis, we will explore the key elements of poetic structure, uncover the significance of poetic devices, and delve into the multifaceted layers of symbolism and metaphor. Prepare to elevate your understanding of poetry as we navigate the path to a comprehensive analysis, unlocking the secrets that lie within the written word.
Analyzing the Structure of a Poem: Lesson 14 Analyzing The Structure Of A Poem Answer Key
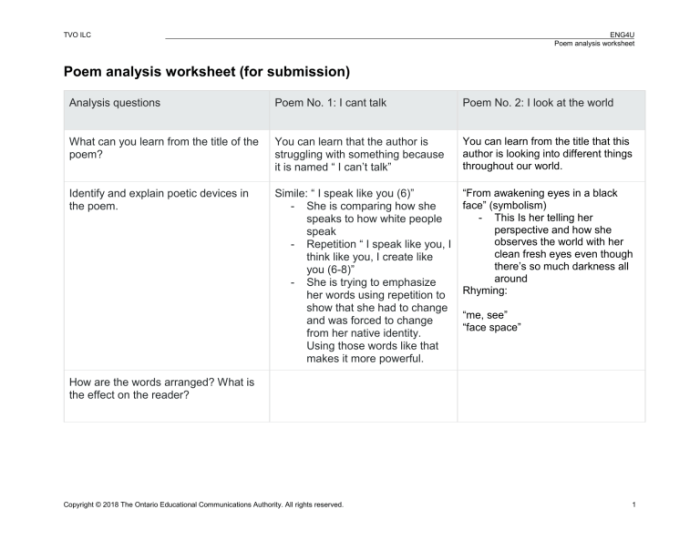
The structure of a poem refers to the way its elements are arranged and organized. It encompasses the number of lines, stanzas, and the pattern of rhyme and rhythm. Analyzing the structure of a poem can provide insights into the poet’s intentions, the poem’s meaning, and its impact on the reader.
There are various types of poetic structures, including:
- Sonnet:A 14-line poem with a specific rhyme scheme and meter.
- Haiku:A three-line poem with a 5-7-5 syllable count.
- Blank verse:A poem written in unrhymed iambic pentameter.
- Free verse:A poem that does not follow any specific rhyme or meter pattern.
The structure of a poem can contribute to its meaning and impact in several ways. For instance, a sonnet’s rigid structure may create a sense of order and control, while a free verse poem’s lack of structure may convey a sense of freedom and spontaneity.
Identifying Poetic Devices

Poetic devices are literary techniques that poets use to enhance the language and imagery of their poems. They can be used to create a variety of effects, such as emphasis, contrast, and surprise.
Some common poetic devices include:
- Metaphor:A comparison between two unlike things without using “like” or “as.”
- Simile:A comparison between two unlike things using “like” or “as.”
- Personification:Giving human qualities to non-human things.
- Imagery:Language that appeals to the senses.
- Symbolism:Using an object or idea to represent something else.
Poetic devices can make a poem more vivid, memorable, and impactful. They can also help to convey complex ideas and emotions in a concise and effective way.
Analyzing Symbolism and Metaphor
Symbolism and metaphor are two important poetic devices that poets use to create deeper layers of meaning in their work. Symbols are objects, images, or ideas that represent something else, while metaphors are comparisons between two unlike things that reveal a hidden similarity.
Symbols can be used to represent a wide range of things, from abstract concepts to concrete objects. For example, a dove may symbolize peace, while a rose may symbolize love. Metaphors can be used to create vivid and memorable images, as well as to reveal hidden truths about the world.
Both symbolism and metaphor can be powerful tools for poets. They can help to create poems that are rich in meaning and that resonate with readers on a deep level.
Exploring Theme and Tone
Theme and tone are two essential elements of poetry. Theme is the central idea or message that the poet is trying to convey, while tone is the poet’s attitude towards the subject matter.
Theme can be expressed explicitly or implicitly in a poem. It can be a simple statement about the human condition, or it can be a more complex exploration of a particular issue or idea.
Tone, on the other hand, is conveyed through the poet’s choice of language and imagery. It can be serious, playful, ironic, or anything in between. Tone can have a significant impact on the meaning and impact of a poem.
Creating a Comprehensive Analysis
When analyzing a poem, it is important to consider all of its elements, including its structure, poetic devices, symbolism, theme, and tone. By doing so, you can gain a deeper understanding of the poem’s meaning and impact.
One way to organize your analysis is to use a structured format, such as the following:
| Element | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Structure | Describe the poem’s structure, including the number of lines, stanzas, and rhyme scheme. |
| Poetic devices | Identify and analyze the poetic devices used in the poem. |
| Symbolism | Identify and analyze the symbols used in the poem. |
| Theme | Identify and analyze the theme of the poem. |
| Tone | Identify and analyze the tone of the poem. |
By following this format, you can create a comprehensive analysis that will help you to understand and appreciate the poem more fully.
Key Questions Answered
What is the significance of structure in poetry?
Structure provides a framework that shapes the poem’s meaning, rhythm, and impact. It influences the flow of ideas, creates emphasis, and contributes to the overall aesthetic experience.
How do poetic devices enhance a poem?
Poetic devices, such as imagery, simile, and metaphor, enrich the language and imagery of a poem. They evoke emotions, create vivid mental pictures, and convey complex ideas in a condensed and impactful manner.
What is the role of symbolism in poetry?
Symbolism allows poets to convey abstract concepts and emotions through concrete objects or images. Symbols create layers of meaning, inviting readers to explore deeper interpretations and connections.