What is the advantage of a wire wound resistor? In the realm of electrical engineering, this question unveils the exceptional capabilities of a resistor type renowned for its ability to manage high power levels. Wire wound resistors stand out in demanding applications, offering unique advantages that make them indispensable in various industries.
Their construction, meticulously crafted from resistive wire wound around an insulating core, grants them exceptional power handling capabilities. This intricate design enables wire wound resistors to dissipate significant amounts of power, making them ideal for applications where high currents and voltages are encountered.
What is a Wire Wound Resistor?: What Is The Advantage Of A Wire Wound Resistor

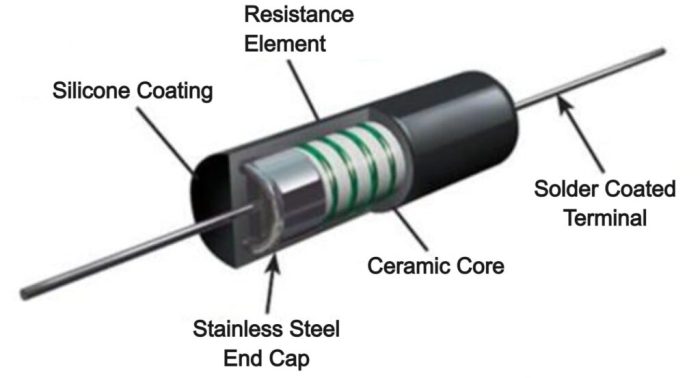
A wire wound resistor is a type of resistor that consists of a resistive wire wound around an insulating core. The wire is typically made of a metal alloy, such as nichrome or manganin, and the core is usually made of ceramic or plastic.
Wire wound resistors are known for their high power handling capabilities and are often used in applications where high currents or voltages are present.
Advantages of Wire Wound Resistors
- High power handling capabilities: Wire wound resistors can handle high power dissipation due to their large surface area and the use of resistive alloys with high melting points.
- High current carrying capacity: The thick wire used in wire wound resistors allows them to carry high currents without overheating.
- High voltage withstand capability: Wire wound resistors can withstand high voltages due to the insulation provided by the core and the spacing between the windings.
Applications and Uses
- High-power circuits: Wire wound resistors are commonly used in high-power circuits, such as power supplies, amplifiers, and motor controllers.
- Voltage dividers: Wire wound resistors are used as voltage dividers to reduce the voltage in a circuit.
- Current sensing: Wire wound resistors can be used to sense current by measuring the voltage drop across them.
Comparison with Other Resistor Types
Compared to other resistor types, wire wound resistors offer superior power handling capabilities. However, they are generally less precise and have a higher temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) than other types of resistors.
- Carbon composition resistors: Carbon composition resistors are less expensive and have a lower TCR than wire wound resistors, but they have a lower power handling capacity.
- Film resistors: Film resistors are more precise and have a lower TCR than wire wound resistors, but they have a lower power handling capacity.
- Metal oxide resistors: Metal oxide resistors have a higher power handling capacity than film resistors, but they are less precise and have a higher TCR.
Design Considerations
When selecting a wire wound resistor, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Power rating: The power rating of the resistor must be greater than the power that will be dissipated in the circuit.
- Resistance value: The resistance value of the resistor must be appropriate for the application.
- Tolerance: The tolerance of the resistor is the maximum deviation from the nominal resistance value.
Manufacturing Process, What is the advantage of a wire wound resistor
The manufacturing process of wire wound resistors involves the following steps:
- Winding the resistive wire around the core
- Insulating the windings with a ceramic or plastic coating
- Applying a protective coating to the resistor
- Testing the resistor to ensure that it meets specifications
FAQ Corner
What sets wire wound resistors apart from other resistor types?
Wire wound resistors excel in power handling capabilities, allowing them to dissipate significant amounts of power compared to other resistor types. Their ability to withstand high currents and voltages further enhances their suitability for demanding applications.
In what industries are wire wound resistors commonly employed?
Wire wound resistors find widespread use in industries such as power electronics, industrial automation, and telecommunications, where reliable power handling and high current carrying capacity are essential.
What factors should be considered when selecting a wire wound resistor?
When selecting a wire wound resistor, key factors to consider include power rating, resistance value, tolerance, and environmental conditions. Proper selection ensures optimal performance and longevity in the intended application.