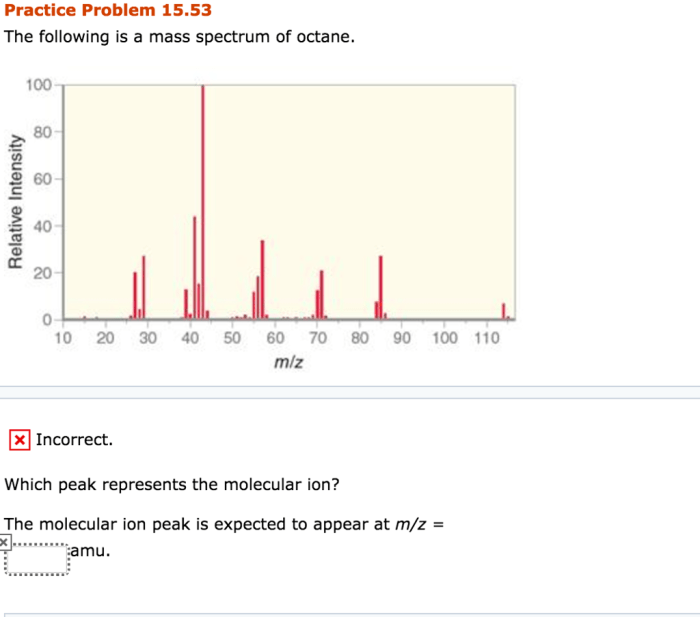
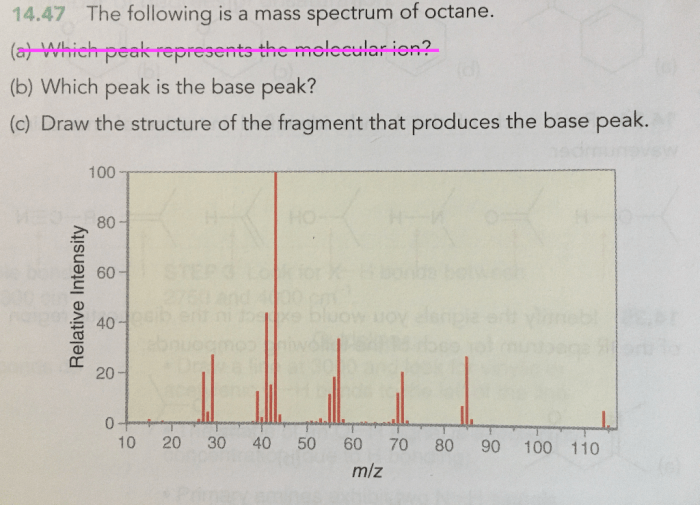
The following is a mass spectrum of octane, a valuable tool for understanding the structure and properties of organic compounds. Mass spectrometry, a powerful analytical technique, provides insights into the molecular composition of substances, enabling researchers to identify and characterize compounds with precision.
This mass spectrum of octane reveals crucial information about its molecular structure and fragmentation patterns, providing a deeper understanding of its chemical properties and applications in various fields.
Mass Spectrometry of Octane
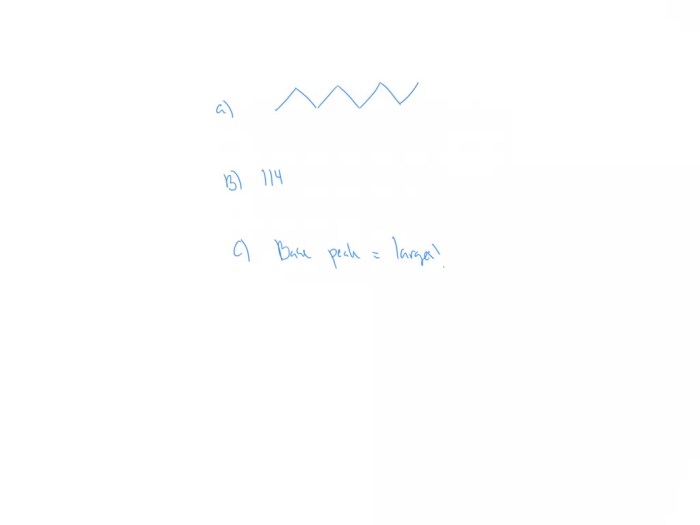
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique used to identify and characterize organic compounds. It involves ionizing the compound and measuring the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of the resulting ions. The mass spectrum of a compound provides a unique fingerprint that can be used to identify and determine its structure.
Octane (C 8H 18) is a hydrocarbon with a molecular weight of 114.23 g/mol. It is a major component of gasoline and is used as a reference fuel for testing engine performance. The mass spectrum of octane is important for understanding its structure and properties, as well as for identifying it in various applications.
Mass Spectrometry of Octane, The following is a mass spectrum of octane
Mass spectrometry of octane involves ionizing the compound using an electron beam or other ionization technique. The resulting ions are then separated according to their m/z ratio using a mass analyzer. The abundance of each ion is plotted against its m/z ratio to produce a mass spectrum.
The mass spectrum of octane shows a molecular ion peak at m/z 114, which corresponds to the molecular weight of the compound. Fragmentation of the molecular ion results in the formation of smaller ions, which are also detected in the mass spectrum.
Interpretation of the Mass Spectrum
The molecular ion peak provides information about the molecular weight of the compound. The fragmentation patterns observed in the mass spectrum can be used to determine the structure of the compound. In the case of octane, the fragmentation patterns indicate the presence of a branched chain structure.
The most abundant fragment ion in the mass spectrum of octane is at m/z 57. This ion corresponds to the tert-butyl cation, which is formed by the loss of a methyl group from the molecular ion. Other fragment ions observed in the mass spectrum include the sec-butyl cation (m/z 43), the isobutyl cation (m/z 57), and the propyl cation (m/z 43).
Applications of Octane Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry of octane is used in various fields, including:
- Fuel analysis:Octane mass spectrometry is used to determine the octane number of gasoline, which is a measure of its resistance to knocking in an engine.
- Environmental monitoring:Octane mass spectrometry is used to detect and quantify octane in environmental samples, such as air and water.
- Chemical research:Octane mass spectrometry is used to study the structure and reactivity of octane and other hydrocarbons.
Popular Questions: The Following Is A Mass Spectrum Of Octane
What is the purpose of a mass spectrum?
A mass spectrum provides a graphical representation of the mass-to-charge ratio of ions produced from a sample, allowing for the identification and characterization of compounds.
What is octane?
Octane is a branched-chain hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C8H18, commonly used as a fuel in internal combustion engines.
Why is analyzing the mass spectrum of octane significant?
Analyzing the mass spectrum of octane provides insights into its molecular structure, fragmentation patterns, and chemical properties, which are crucial for understanding its behavior and applications.