As “Introduction to Energy Worksheet Answers” takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world of energy concepts, sources, production, consumption, and environmental impact. With a focus on clarity and precision, this comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of energy, providing a solid foundation for understanding its multifaceted nature.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic.
1. Introduction to Energy Concepts

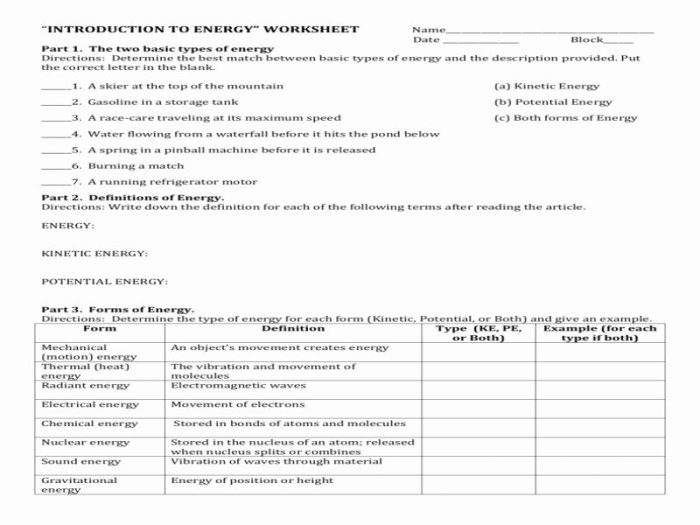
Energy is the ability to do work. It exists in various forms, including kinetic energy (energy of motion), potential energy (stored energy), heat energy, and electrical energy. Energy can be transformed from one form to another. For instance, burning fossil fuels releases chemical energy that is converted into heat energy, which in turn can be used to generate electricity (electrical energy).
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed. This means that the total amount of energy in the universe remains constant.
2. Energy Sources and their Types
Energy sources can be classified as renewable or non-renewable. Renewable energy sources are replenished naturally, such as solar energy, wind energy, and geothermal energy. Non-renewable energy sources are finite, such as fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) and nuclear energy.
| Energy Source | Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fossil Fuels | Non-Renewable | Abundant, reliable, affordable | Polluting, limited supply |
| Nuclear Energy | Non-Renewable | High energy density, low carbon emissions | Radioactive waste, high cost |
| Solar Energy | Renewable | Clean, sustainable, abundant | Intermittent, requires large land area |
| Wind Energy | Renewable | Clean, sustainable, abundant | Intermittent, requires large turbines |
3. Energy Production and Distribution
Energy is generated from different sources using various technologies. For example, fossil fuels are burned to produce heat, which drives turbines to generate electricity. Nuclear energy involves nuclear fission or fusion to release energy. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, use photovoltaic cells or turbines to convert sunlight or wind energy into electricity.
Energy is distributed through power plants and transmission lines. Power plants generate electricity, which is then transmitted to homes, businesses, and industries via transmission lines. Energy efficiency measures aim to reduce energy consumption and waste, such as using energy-efficient appliances and insulation.
4. Energy Consumption and Conservation
Global energy consumption has been increasing steadily due to population growth, economic development, and technological advancements. Factors influencing energy consumption include population size, industrialization, and energy efficiency.
Energy conservation strategies focus on reducing waste and promoting energy-efficient practices. This can involve using energy-efficient lighting, appliances, and transportation systems. Additionally, reducing energy consumption can help mitigate environmental impacts.
5. Environmental Impact of Energy Production
Energy production from different sources can have significant environmental impacts. Fossil fuels contribute to air pollution (e.g., carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides), water pollution (e.g., oil spills), and climate change. Nuclear energy produces radioactive waste that requires careful disposal.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, have minimal environmental impacts. They offer a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels and help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Balancing energy production with environmental protection is crucial for a sustainable future.
Helpful Answers: Introduction To Energy Worksheet Answers
What is energy?
Energy is a fundamental property of the universe that enables objects to do work or undergo change.
What are the different forms of energy?
Energy exists in various forms, including kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, electrical energy, and chemical energy.
What is the law of conservation of energy?
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.