Cleft palate hesi case study, a captivating exploration into the intricacies of cleft palate care, invites nurses to delve into a comprehensive analysis of patient management, nursing interventions, and ethical considerations surrounding this complex condition.
This case study presents a unique opportunity to gain a holistic understanding of cleft palate, its impact on patients and their families, and the essential role of nurses in providing compassionate and effective care.
Cleft Palate Overview
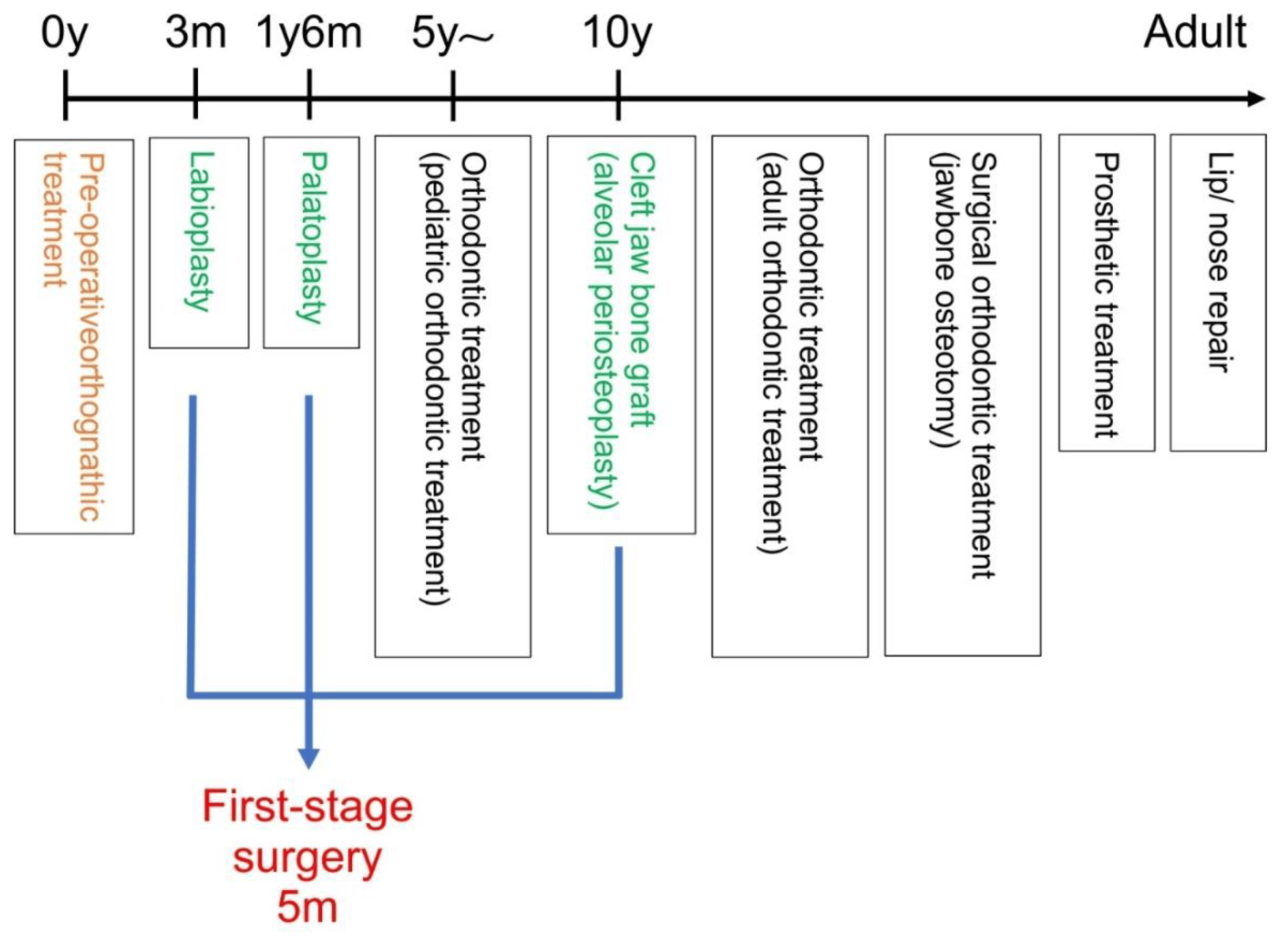
Cleft palate is a birth defect that occurs when the roof of the mouth does not close completely during pregnancy. This can result in a gap or opening in the palate, which can affect a child’s ability to eat, speak, and hear.Cleft
palate can range from a small opening in the soft palate to a complete separation of the hard and soft palates. The severity of the cleft can vary depending on the size and location of the opening.The exact cause of cleft palate is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Some risk factors for cleft palate include:
- Family history of cleft palate
- Certain medications taken during pregnancy, such as anti-seizure medications
- Exposure to certain chemicals, such as alcohol and tobacco smoke
- Nutritional deficiencies, such as folic acid deficiency
HESI Case Study
A 3-month-old infant is brought to the clinic by their parents for a well-baby checkup. During the examination, the nurse notices a cleft palate.
The nurse should assess the infant’s feeding history, weight gain, and overall health. The nurse should also provide the parents with information about cleft palate, including the different types of clefts, the causes of cleft palate, and the treatment options available.
Relevant Patient Information
- Age: 3 months
- Sex: Not specified
- Chief complaint: Cleft palate
- Medical history: Not specified
- Family history: Not specified
- Social history: Not specified
Potential Nursing Interventions
The nurse should provide the parents with information about cleft palate, including the different types of clefts, the causes of cleft palate, and the treatment options available.
The nurse should also provide the parents with support and resources, such as support groups and websites, to help them cope with the challenges of raising a child with a cleft palate.
- Assess the infant’s feeding history, weight gain, and overall health.
- Provide the parents with information about cleft palate.
- Provide the parents with support and resources.
- Refer the infant to a specialist for further evaluation and treatment.
Nursing Management
Nursing management of patients with cleft palate involves pre-operative and post-operative care, as well as monitoring for potential complications.
Pre-operative Care
Pre-operative care focuses on optimizing the patient’s condition before surgery. This includes:
- Nutritional assessment and support
- Ensuring adequate hydration
- Administering antibiotics to prevent infection
- Providing emotional support to the patient and family
Post-operative Care
Post-operative care aims to promote healing and prevent complications. It includes:
- Monitoring vital signs and pain levels
- Administering pain medication as prescribed
- Providing oral care to prevent infection
- Ensuring adequate nutrition and hydration
- Monitoring for signs of infection or other complications
Potential Complications
Potential complications of cleft palate surgery include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Scarring
- Velopharyngeal insufficiency (VPI), which can lead to speech problems
- Dental problems
Patient Education
Patient education is crucial for individuals with cleft palate, empowering them to manage their condition effectively. It enhances their understanding of the disorder, treatment options, and self-care practices.
Topics to Cover
Patient education should encompass various topics, including:
- Cleft palate anatomy and causes
- Types of cleft palate and their associated challenges
- Treatment options, including surgery, speech therapy, and orthodontics
- Post-operative care and recovery
- Nutritional guidelines and feeding techniques
- Speech and language development
- Dental hygiene and oral health
- Emotional and social support
Resources for Patient Support
Several organizations provide resources and support for individuals with cleft palate, including:
- American Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Association (ACPA): www.cleftline.org
- Smile Train: www.smiletrain.org
- Operation Smile: www.operationsmile.org
These organizations offer information, support groups, and financial assistance to help individuals and families navigate the challenges associated with cleft palate.
To get a better understanding of cleft palate hesi case study, it’s important to examine various perspectives. One such resource is the omega psi phi district map . This map provides valuable insights into the geographical distribution of the organization, which can help researchers understand the potential impact of cleft palate on different communities.
By exploring these connections, we can gain a more comprehensive view of the topic and develop more effective strategies for addressing this condition.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Cleft Palate Hesi Case Study
Effective management of cleft palate involves a collaborative approach among healthcare professionals. Teamwork ensures comprehensive care, leveraging diverse expertise to improve patient outcomes.
Role of Other Healthcare Professionals
- Plastic Surgeons:Perform surgeries to repair the cleft lip and palate.
- Otolaryngologists:Address ear, nose, and throat issues related to cleft palate, such as hearing loss and speech problems.
- Pediatricians:Provide overall medical care, monitoring growth and development.
- Speech-Language Pathologists:Evaluate and treat speech and language difficulties.
- Dentists and Orthodontists:Manage dental issues and orthodontic treatment.
- Social Workers:Provide emotional support, counseling, and resource navigation for families.
- Dietitians:Ensure proper nutrition and feeding techniques for infants with cleft palate.
Importance of Teamwork, Cleft palate hesi case study
Teamwork is crucial for:
- Developing a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual patient’s needs.
- Ensuring continuity of care throughout the treatment journey.
- Addressing the multifaceted challenges associated with cleft palate, including physical, developmental, and psychosocial aspects.
Interdisciplinary Interventions
- Team Meetings:Regular meetings facilitate communication, coordination, and shared decision-making.
- Case Management:A dedicated case manager coordinates care, tracks progress, and advocates for the patient’s needs.
- Multidisciplinary Clinics:Offer comprehensive services in one location, reducing the need for multiple appointments.
- Shared Medical Records:Secure platforms allow healthcare providers to access and share patient information seamlessly.
Cultural Considerations
Cultural factors play a significant role in healthcare, as they can influence beliefs, values, and behaviors related to health and illness. Understanding and addressing cultural factors is crucial for providing culturally competent care that is tailored to the needs of diverse patient populations.
When caring for patients with cleft palate, it is important to be aware of the cultural beliefs and practices that may impact their care. For example, in some cultures, cleft palate is associated with superstition or stigma, which can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Role of Cultural Sensitivity
Cultural sensitivity is the ability to understand and appreciate the cultural differences that exist between people. It involves recognizing that there is no one right way to do things and that what may be considered normal in one culture may be considered strange or even offensive in another.
In the context of healthcare, cultural sensitivity is essential for providing care that is respectful of the patient’s cultural background and beliefs. This includes understanding the patient’s communication style, values, and beliefs about health and illness.
Strategies for Providing Culturally Competent Care
- Be aware of your own cultural biases and assumptions.Everyone has cultural biases and assumptions, but it is important to be aware of them so that you can avoid letting them interfere with your care of patients.
- Learn about the cultural beliefs and practices of your patients.There are many resources available to help you learn about different cultures, including books, articles, and websites. You can also talk to your patients about their cultural beliefs and practices.
- Be respectful of your patients’ cultural beliefs and practices.Even if you do not agree with your patients’ cultural beliefs and practices, it is important to respect them. This means listening to your patients and trying to understand their point of view.
- Provide care that is tailored to the needs of your patients.When providing care, it is important to consider the cultural beliefs and practices of your patients. This may mean modifying your care plan to accommodate their beliefs and practices.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are of paramount importance in cleft palate care. These principles guide healthcare professionals in providing comprehensive and compassionate treatment while respecting patient autonomy and well-being.
Informed consent is a cornerstone of ethical care. Patients and their families must be fully informed about the nature of the condition, treatment options, potential risks, and benefits. They should have ample opportunity to ask questions and make informed decisions about their care.
Ethical Dilemmas
Ethical dilemmas can arise in cleft palate care, particularly when treatment decisions involve trade-offs between different values or principles. For example:
- Timing of surgery:The optimal timing of surgery for cleft palate repair can vary depending on the individual patient’s needs and preferences. Balancing the potential benefits of early surgery with the risks of anesthesia and potential complications can pose ethical challenges.
- Speech therapy:Speech therapy is essential for improving communication skills in children with cleft palate. However, it can be a lengthy and demanding process. Deciding on the appropriate intensity and duration of therapy while considering the child’s needs and family resources can present ethical considerations.
- Psychological support:Children with cleft palate may face social and emotional challenges. Ensuring they receive adequate psychological support while respecting their privacy and confidentiality is an ethical responsibility of healthcare professionals.
FAQ Compilation
What is the most common type of cleft palate?
The most common type of cleft palate is an isolated cleft palate, which occurs without other facial deformities.
What are the potential complications of cleft palate surgery?
Potential complications of cleft palate surgery include bleeding, infection, and speech problems.
What is the role of the nurse in cleft palate care?
The nurse plays a vital role in cleft palate care, providing pre- and post-operative care, patient education, and support to patients and their families.