Mayan inca and aztec map – Delve into the fascinating world of Mayan, Inca, and Aztec maps, where ancient civilizations meticulously charted their territories and beliefs. These intricate creations provide a glimpse into their cultural, geographical, and cartographic ingenuity.
From the intricate glyphs of the Mayans to the knotted strings of the Incas and the pictorial codices of the Aztecs, these maps reveal the diverse perspectives and techniques employed by these pre-Columbian societies.
Map Comparison
Mayan, Inca, and Aztec civilizations developed distinct mapping styles to represent their territories and landscapes. These maps shared similarities in their use of symbolic imagery and focus on geographic features, but they also differed in their materials, scales, and specific conventions.
All three civilizations used natural materials like bark cloth, animal skin, and stone for their maps. However, the Mayans were known for their elaborate codices, or folded books, which contained painted maps and written text. The Incas used knotted strings called quipus to record information, including geographic data.
The Aztecs created maps on large sheets of cotton cloth or animal skin.
Symbols and Conventions
The symbols used on these maps varied depending on the civilization. Mayan maps often featured stylized glyphs representing cities, rivers, and mountains. Inca maps used geometric shapes and lines to indicate roads, canals, and agricultural terraces. Aztec maps employed a combination of pictorial and symbolic elements, including images of temples, animals, and deities.
Scale and Accuracy
The scale and accuracy of these maps also varied. Mayan maps tended to be more abstract and less precise than Inca or Aztec maps. Inca maps were often large-scale and highly detailed, showing the extent of their vast empire. Aztec maps were more focused on local areas and were often used for practical purposes such as planning military campaigns.
Cultural Significance
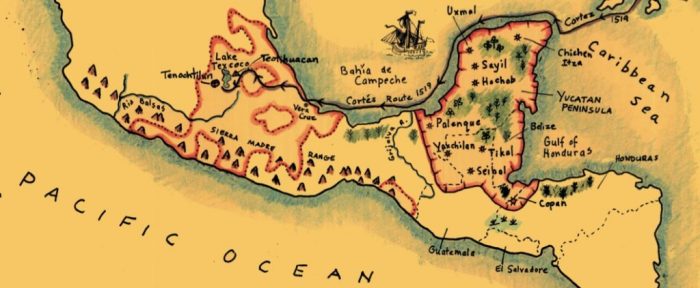
The ancient maps of the Maya, Inca, and Aztec civilizations provide valuable insights into their respective cultures, histories, and beliefs. These maps served not only as navigational tools but also held deep cultural and religious significance.
For the Maya, maps played a crucial role in their advanced understanding of astronomy and timekeeping. They used star charts to track the movements of celestial bodies and create calendars that accurately predicted astronomical events.
Religious Beliefs
In the Inca Empire, maps were closely tied to religious beliefs and territorial claims. The Inca believed that their empire was the center of the world, and their maps reflected this worldview. They used knotted cords called quipus to record and transmit information, including geographical data and religious narratives.
Geographical Representation
The Mayan, Inca, and Aztec maps showcase distinct approaches to representing the surrounding environment, reflecting the unique cultural and geographical contexts of each civilization.
In terms of scale and orientation, these maps exhibit varying degrees of accuracy and precision. While some maps provide detailed depictions of specific regions, others offer more general overviews.
Mayan Maps
- Orientation:Mayan maps typically display an east-west orientation, with the cardinal directions indicated by symbols or glyphs.
- Scale:Mayan maps often lack a consistent scale, making it challenging to determine the precise distances between landmarks.
- Landmarks:Mayan maps include representations of important landmarks, such as cities, temples, and water bodies, providing a valuable glimpse into the geography of their settlements.
Inca Maps
- Orientation:Inca maps are primarily oriented towards the capital city of Cusco, reflecting the centralized nature of the Inca Empire.
- Scale:Inca maps exhibit a more consistent scale compared to Mayan maps, allowing for more accurate measurements of distances.
- Landmarks:Inca maps feature a wide range of landmarks, including roads, bridges, and agricultural terraces, showcasing the advanced infrastructure and agricultural practices of the Inca civilization.
Aztec Maps
- Orientation:Aztec maps often display a north-south orientation, with the cardinal directions indicated by symbols or colors.
- Scale:Aztec maps vary in scale, with some maps providing detailed depictions of specific regions and others offering more general overviews.
- Landmarks:Aztec maps include representations of important landmarks, such as canals, temples, and markets, reflecting the urban and commercial nature of Aztec society.
Cartographic Techniques: Mayan Inca And Aztec Map
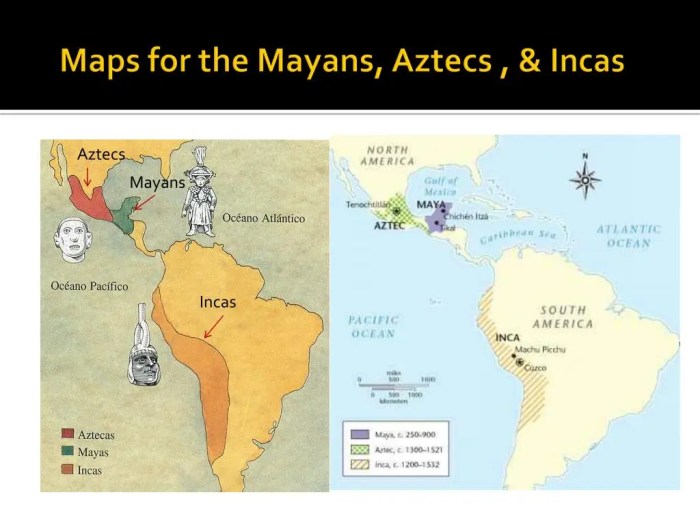
The Mayans, Incas, and Aztecs employed distinct cartographic techniques to represent their respective territories and convey geographical information.
Grids, glyphs, and other symbols played significant roles in their mapmaking practices, reflecting the cultural and technological advancements of each civilization.
Grids and Glyphs
The Mayans utilized a sophisticated grid system to create accurate maps. They aligned their grids with cardinal directions, allowing for precise measurements and the depiction of complex geographical features. Glyphs, representing various geographical elements such as mountains, rivers, and cities, were placed within the grid cells.
Inca Knotted Cords
The Incas, on the other hand, employed knotted cords known as quipus to record and transmit information, including geographical data. Quipus consisted of colored strings with knots tied at specific intervals. Each knot represented a numerical value, and the position and color of the knot indicated the type of information being conveyed.
Aztec Pictorial Maps
The Aztecs created pictorial maps known as codices. These maps were highly detailed and incorporated elements of art and symbolism. They depicted the landscape, settlements, and cultural landmarks with a focus on historical events and religious significance.
Historical Context

The Mayan, Inca, and Aztec maps were created during distinct time periods and in different geographic regions, reflecting the political and social contexts of their respective civilizations.
The Mayan civilization flourished in Mesoamerica from the 3rd century BCE to the 10th century CE, primarily in the present-day regions of southern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, and western Honduras.
Mayan Maps
- Created between the 8th and 10th centuries CE.
- Used for religious and political purposes, depicting the cosmos and sacred landscapes.
- Influenced by the Maya’s advanced astronomical knowledge and their complex religious beliefs.
The Inca Empire emerged in the Andes region of South America in the 13th century CE, expanding to encompass present-day Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador, and parts of Chile and Argentina.
Inca Maps
- Created during the 15th and 16th centuries CE.
- Used for administrative and military purposes, mapping the vast Inca road network and settlements.
- Reflect the Inca’s highly centralized and bureaucratic state structure.
The Aztec Empire arose in central Mexico in the 14th century CE, eventually controlling much of Mesoamerica.
Aztec Maps
- Created in the 16th century CE.
- Used for political and economic purposes, depicting the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan, and its surrounding territories.
- Reflect the Aztec’s advanced urban planning and their extensive trade networks.
Modern Interpretations

Modern scholarship has greatly contributed to the interpretation and utilization of ancient Mayan, Inca, and Aztec maps. These maps have provided valuable insights into the cultural, geographical, and historical aspects of these civilizations.Scholars have utilized these maps to reconstruct ancient landscapes, understand trade routes, and study settlement patterns.
They have also aided in deciphering ancient writing systems and interpreting religious beliefs and practices.
The intricate maps created by the Maya, Inca, and Aztec civilizations showcase their advanced knowledge and artistry. These maps offer insights into their urban planning, trade routes, and spiritual beliefs. Transitioning to a different topic, if you’re looking to test your mathematical prowess, check out the calculus ab unit 1 test . Returning to the topic of ancient maps, the Maya, Inca, and Aztec maps continue to captivate historians and scholars alike, providing a glimpse into the rich cultural heritage of these ancient civilizations.
Ongoing Debates and Controversies, Mayan inca and aztec map
Despite their significance, the accuracy and significance of these maps remain subjects of ongoing debates and controversies. Some scholars argue that these maps are highly accurate representations of the ancient world, while others question their precision and suggest they may have been influenced by cultural beliefs and symbolism.Another
debate centers around the extent to which these maps were used for practical purposes, such as navigation or land management. While some believe they were primarily symbolic or ceremonial, others argue that they had a more practical function in daily life.These
debates and controversies continue to drive scholarly research and contribute to our understanding of the ancient civilizations that created these remarkable maps.
Comparative Table
The following table provides a comparison of key features of Mayan, Inca, and Aztec maps:
Materials
- Mayan: bark paper, animal skins
- Inca: knotted cords (quipus), cloth
- Aztec: bark paper, animal skins
Symbols
- Mayan: pictographs, hieroglyphs
- Inca: geometric shapes, colors
- Aztec: pictograms, ideograms
Scale
- Mayan: varied, from large-scale regional maps to small-scale town plans
- Inca: large-scale, covering vast territories
- Aztec: medium-scale, focusing on central Mexico
Accuracy
- Mayan: generally accurate, but some distortions for symbolic purposes
- Inca: highly accurate, with detailed measurements and surveying techniques
- Aztec: relatively accurate, but with some exaggerations and distortions
Cultural Significance
- Mayan: used for religious, political, and economic purposes
- Inca: used for administrative, military, and religious purposes
- Aztec: used for taxation, land distribution, and military planning
Visual Examples
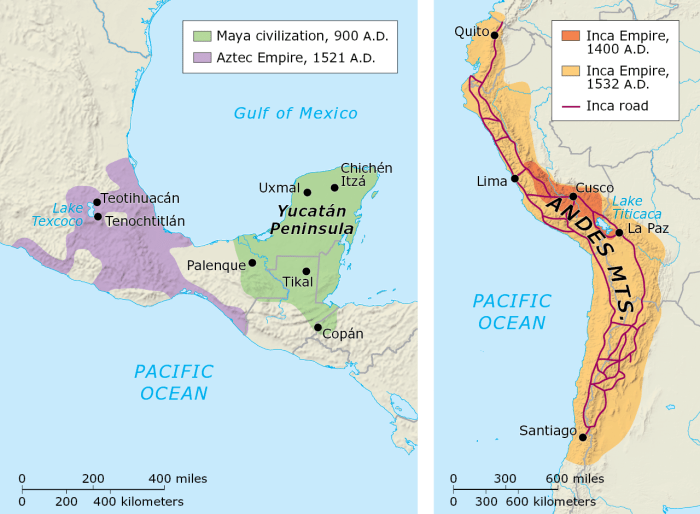
The maps of the Maya, Inca, and Aztec civilizations offer valuable insights into their cultures, geographical knowledge, and cartographic techniques. These maps provide visual representations of their territories, showcasing their understanding of the world and their place within it.
The following are representative maps from each civilization, along with detailed captions describing their content and significance:
Maya Dresden Codex
- The Dresden Codex is a Maya manuscript dating from the 13th century CE.
- It contains a detailed map of the Maya city of Chichen Itza and its surrounding areas.
- The map shows the city’s temples, palaces, and other structures, as well as its canals and roads.
- It also includes glyphs and symbols that provide information about the city’s history and culture.
Inca Quipu
- The Inca Quipu is a system of knotted cords used by the Inca civilization to record information.
- It was used for a variety of purposes, including accounting, communication, and mapping.
- Quipus could represent complex geographical information, such as the layout of roads, settlements, and agricultural fields.
- The quipu system was highly sophisticated and allowed for the storage and transmission of large amounts of data.
Aztec Codex Mendoza
- The Codex Mendoza is an Aztec manuscript dating from the 16th century CE.
- It contains a series of maps depicting the Aztec Empire and its provinces.
- The maps show the location of cities, towns, and other settlements, as well as the boundaries of the empire.
- They also include symbols and glyphs that provide information about the history and culture of the Aztec people.
Q&A
What are the main differences between Mayan, Inca, and Aztec maps?
Mayan maps were primarily pictorial, featuring elaborate glyphs and symbols. Inca maps used knotted strings called quipus to record information, while Aztec maps combined pictorial and symbolic elements.
How did these maps contribute to the cultural and historical development of these civilizations?
Maps played a crucial role in navigation, territorial claims, and religious beliefs. They facilitated trade, exploration, and the expansion of empires.
What are some of the challenges in interpreting these ancient maps?
Due to the passage of time and cultural differences, some symbols and glyphs remain undeciphered, making it challenging to fully understand the intended meanings.